
난이도: Hard
Problem Description
There is an undirected weighted graph with n vertices labeled from 0 to n - 1.
You are given the integer n and an array edges, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between vertices ui and vi with a weight of wi.
A walk on a graph is a sequence of vertices and edges. The walk starts and ends with a vertex, and each edge connects the vertex that comes before it and the vertex that comes after it. It's important to note that a walk may visit the same edge or vertex more than once.
The cost of a walk starting at node u and ending at node v is defined as the bitwise AND of the weights of the edges traversed during the walk. In other words, if the sequence of edge weights encountered during the walk is w0, w1, w2, ..., wk, then the cost is calculated as w0 & w1 & w2 & ... & wk, where & denotes the bitwise AND operator.
You are also given a 2D array query, where query[i] = [si, ti]. For each query, you need to find the minimum cost of the walk starting at vertex si and ending at vertex ti. If there exists no such walk, the answer is -1.
Return the array answer, where answer[i] denotes the minimum cost of a walk for query i.
Problem Example
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,7],[1,3,7],[1,2,1]], query = [[0,3],[3,4]]
Output: [1,-1]
Explanation:
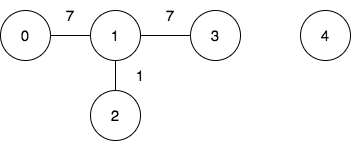
To achieve the cost of 1 in the first query, we need to move on the following edges: 0->1 (weight 7), 1->2 (weight 1), 2->1 (weight 1), 1->3 (weight 7).
In the second query, there is no walk between nodes 3 and 4, so the answer is -1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,2,7],[0,1,15],[1,2,6],[1,2,1]], query = [[1,2]]
Output: [0]
Explanation:
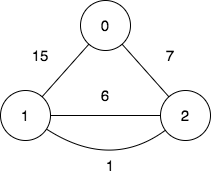
To achieve the cost of 0 in the first query, we need to move on the following edges: 1->2 (weight 1), 2->1 (weight 6), 1->2 (weight 1).
Constraints
2 <= n <= 1050 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= wi <= 1051 <= query.length <= 105query[i].length == 20 <= si, ti <= n - 1si != ti
✏️ Solution
class Solution:
def minimumCost(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], query: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
and_result = [-1] * n
def find(parent, x):
if parent[x] != x:
parent[x] = find(parent, parent[x])
return parent[x]
def union(parent, x, y, cost):
root_x = find(parent, x)
root_y = find(parent, y)
and_result[root_x] &= cost & and_result[root_y]
and_result[root_y] = and_result[root_x]
if root_x < root_y:
parent[root_y] = root_x
else:
parent[root_x] = root_y
parent = list(range(n))
for v1, v2, cost in edges:
union(parent, v1, v2, cost)
answer = []
for v1, v2 in query:
root_x = find(parent, v1)
root_y = find(parent, v2)
if root_x == root_y:
answer.append(and_result[root_x])
else:
answer.append(-1)
return answerUnion-Find를 응용해서 풀 수 있는 좋은 문제였던 것 같다.
먼저 Union-Find로 그래프를 연결된 컴포넌트 단위로 관리했다.
find 함수와 union 함수를 통해 같은 그룹인지 판별했고, 각 연결된 컴포넌트 내에서 AND 연산을 유지했다.
즉, and_result 배열을 사용하여 해당 그룹의 모든 간선 가중치의 AND 값을 유지했다.
쿼리 처리 시 같은 컴포넌트 여부를 확인했다. 같은 그룹이면 and_result[root_x]를 answer에 append 하였고, 같은 그룹이 아니면 -1를 answer에 append했다.
마지막에는 이러한 answer를 반한하여 정답을 맞출 수 있었다.
⚙️ Runtime & Memory

문제: 3108. Minimum Cost Walk in Weighted Graph
깃허브: github
algorithmPractice/LeetCode/3348-minimum-cost-walk-in-weighted-graph at main · laewonJeong/algorithmPractice
하루 한 문제 챌린지. Contribute to laewonJeong/algorithmPractice development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 3169. Count Days Without Meetings (Python) (0) | 2025.03.24 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 1976. Number of Ways to Arrive at Destination (Python) (0) | 2025.03.23 |
| [LeetCode] 2401. Longest Nice Subarray (Python) (0) | 2025.03.18 |
| [LeetCode] 2206. Divide Array Into Equal Pairs (Python) (0) | 2025.03.17 |
| [LeetCode] 2594. Minimum Time to Repair Cars (Python) (0) | 2025.03.16 |