
난이도: Medium
문제 설명
There is a directed graph of n nodes with each node labeled from 0 to n - 1. The graph is represented by a 0-indexed 2D integer array graph where graph[i] is an integer array of nodes adjacent to node i, meaning there is an edge from node i to each node in graph[i].
A node is a terminal node if there are no outgoing edges. A node is a safe node if every possible path starting from that node leads to a terminal node (or another safe node).
Return an array containing all the safe nodes of the graph. The answer should be sorted in ascending order.
문제 예제
Example 1:
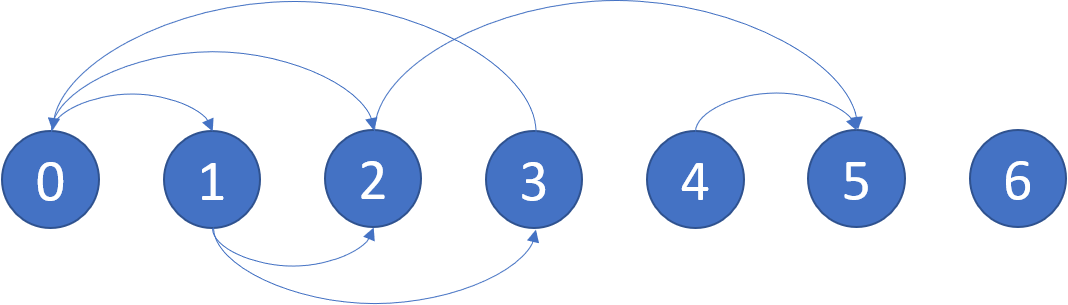
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
Output: [2,4,5,6]
Explanation: The given graph is shown above.
Nodes 5 and 6 are terminal nodes as there are no outgoing edges from either of them.
Every path starting at nodes 2, 4, 5, and 6 all lead to either node 5 or 6.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[1,2,3,4],[1,2],[3,4],[0,4],[]]
Output: [4]
Explanation:
Only node 4 is a terminal node, and every path starting at node 4 leads to node 4.
제한 사항
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 1040 <= graph[i].length <= n0 <= graph[i][j] <= n - 1graph[i]is sorted in a strictly increasing order.- The graph may contain self-loops.
- The number of edges in the graph will be in the range
[1, 4 * 104].
Solution(솔루션)
class Solution:
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
n = len(graph)
graph_reverse = [[] for _ in range(n)]
q = deque([])
answer = []
for i in range(n):
if len(graph[i]) == 0:
q.append(i)
for v in graph[i]:
graph_reverse[v].append(i)
while q:
vertex = q.popleft()
answer.append(vertex)
for v in graph_reverse[vertex]:
graph[v].remove(vertex)
if len(graph[v]) == 0:
q.append(v)
return sorted(answer)
터미널 노드가 세이프노드이기 때문에 이를 기준으로 이어진 노드들을 보며 세이프노드를 찾으면 될 것 같았다.
그래서 indegree를 기준으로 graph_reverse를 만들었다. 기존 graph는 out degree기반으로 되어있기 때문이다.
그리고 만약 outgoing degree가 없다고 한다면 q에 vertex index를 넣어주었다.
이제 q에서 vertex index를 pop하여 answer리스트에 넣어주었다.
그리고, 이 vertex와 연결된 이웃 vertex를 확인하여 이 역시 세이프 노드인지 확인했다.
세이프노드가 맞다면 q에 vertex_index를 넣어주었다.
이를 q가 빌 때까지 반복하였고, 마지막에는 answer 리스트를 정렬하고 return하여 정답을 맞출 수 있었다.
문제: 802. Find Eventual Safe States
깃허브: github
algorithmPractice/LeetCode/820-find-eventual-safe-states at main · laewonJeong/algorithmPractice
하루 한 문제 챌린지. Contribute to laewonJeong/algorithmPractice development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 1462. Course Schedule IV (Python) (0) | 2025.01.27 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 2948. Make Lexicographically Smallest Array by Swapping Elements (Python) (0) | 2025.01.25 |
| [LeetCode] 1267. Count Servers that Communicate (Python) (0) | 2025.01.23 |
| [LeetCode] 1765. Map of Highest Peak (Python) (0) | 2025.01.22 |
| [LeetCode] 2017. Grid Game (Python) (0) | 2025.01.21 |