| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- DP
- 아파치 스파크
- Apache Spark
- 도커
- 분산처리
- 우선순위큐
- 카프카
- Apache Hadoop
- 이진탐색
- 아파치 카프카
- docker
- 문자열
- 리트코드
- 알고리즘
- 분산
- 프로그래머스
- 코딩테스트
- KAFKA
- String
- 아파치 하둡
- programmers
- Data Engineering
- leetcode
- 티스토리챌린지
- 오블완
- apache kafka
- Python
- 하둡
- 파이썬
- heapq
- Today
- Total
래원
[LeetCode] 1368. Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid (Python) 본문
[LeetCode] 1368. Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid (Python)
Laewon Jeong 2025. 1. 18. 12:18
난이도: Hard
문제 설명
Given an m x n grid. Each cell of the grid has a sign pointing to the next cell you should visit if you are currently in this cell. The sign of grid[i][j] can be:
- 1 which means go to the cell to the right. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i][j + 1])
- 2 which means go to the cell to the left. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i][j - 1])
- 3 which means go to the lower cell. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i + 1][j])
- 4 which means go to the upper cell. (i.e go from grid[i][j] to grid[i - 1][j])
Notice that there could be some signs on the cells of the grid that point outside the grid.
You will initially start at the upper left cell (0, 0). A valid path in the grid is a path that starts from the upper left cell (0, 0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1) following the signs on the grid. The valid path does not have to be the shortest.
You can modify the sign on a cell with cost = 1. You can modify the sign on a cell one time only.
Return the minimum cost to make the grid have at least one valid path.
문제 예제
Example 1:
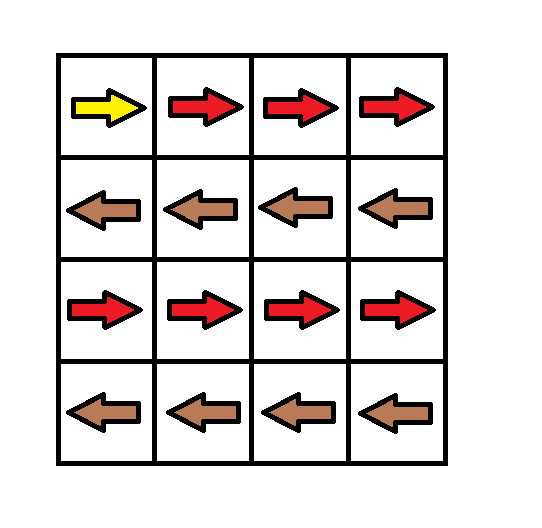
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]]
Output: 3
Explanation: You will start at point (0, 0).
The path to (3, 3) is as follows. (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (3, 3)
The total cost = 3.
Example 2:
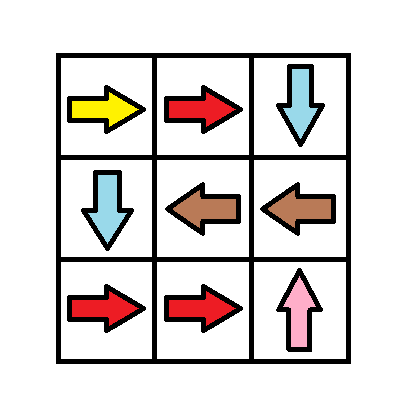
Input: grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]]
Output: 0
Explanation: You can follow the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2).
Example 3:
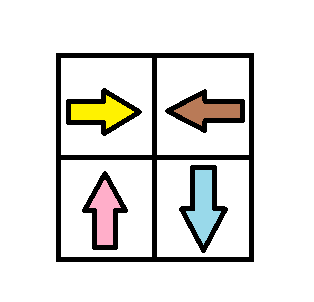
Input: grid = [[1,2],[4,3]]
Output: 1
제한 사항
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 100
- 1 <= grid[i][j] <= 4
✏️ Solution(솔루션)
class Solution:
def minCost(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
visited = defaultdict(bool)
visited[(0,0,0)] = True
moves = [[], [0, 1], [0, -1], [1,0], [-1,0]]
q = [(0,0,0)]
heapq.heapify(q)
while q:
cost, x, y = heapq.heappop(q)
if x == n-1 and y == m-1:
return cost
for i in range(1, 5):
nx = x + moves[i][0]
ny = y + moves[i][1]
if 0<= nx < n and 0<=ny<m:
if i == grid[x][y]:
if not visited[(cost, nx, ny)]:
visited[(cost, nx, ny)] = True
heapq.heappush(q, (cost, nx, ny))
else:
if not visited[(cost+1, nx, ny)]:
visited[(cost+1, nx, ny)] = True
heapq.heappush(q, (cost+1, nx, ny))
나는 이 문제를 bfs로 해결했다.
0, 0 좌표에서 시작해서 상하좌우로 모두 움직여 만약 grid[x][y]와 미리 만들어둔 moves의 인덱스와 같다면 cost를 그대로 두고 아니라고 한다면 cost에 +1을 해주어 관리했다.
그리고 문제는 최소한의 cost를 return해야하기 때문에 deque를 사용하는 것이 아닌 heapq를 사용해서 작은 cost를 갖는 애들로 먼저 연산을 수행했다.
연산을 계속 수행하다가 q에서 pop한 x,y값이 n-1, m-1이면 cost를 반환하고 정답을 맞출 수 있었다.
이 코드는 수행시간이 다른사람들에 비해 오래걸리긴 했다. 좀 더 효율적이게 한번 더 짜봐야할 것 같다.
문제: 1368. Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid
깃허브: github
algorithmPractice/LeetCode/1485-minimum-cost-to-make-at-least-one-valid-path-in-a-grid at main · laewonJeong/algorithmPractice
하루 한 문제 챌린지. Contribute to laewonJeong/algorithmPractice development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'알고리즘 > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 2661. First Completely Painted Row or Column (Python) (0) | 2025.01.20 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II (Python) (0) | 2025.01.20 |
| [LeetCode] 2683. Neighboring Bitwise XOR (Python) (0) | 2025.01.17 |
| [LeetCode] 2425. Bitwise XOR of All Pairings (Python) (0) | 2025.01.16 |
| [LeetCode] 2429. Minimize XOR (Python) (0) | 2025.01.15 |